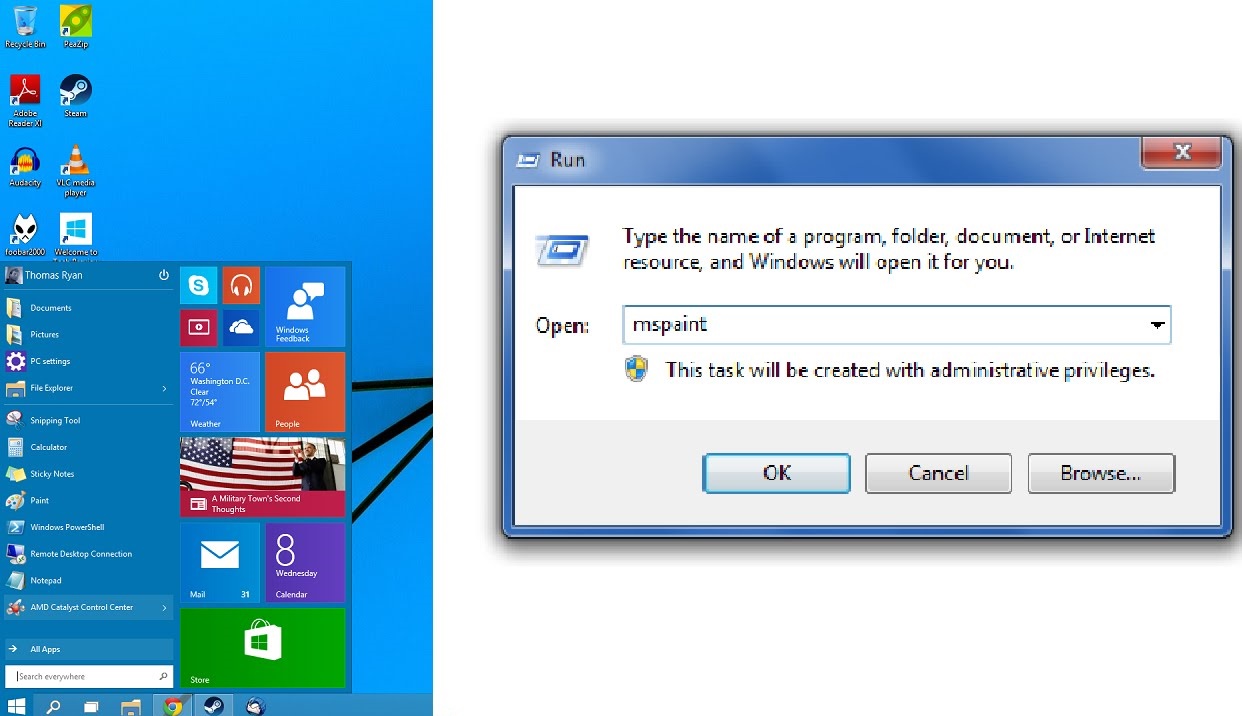
Windows 10 Run Commands
Although most day-to-day tasks in Windows can be accomplished via the standard graphical user interface, a tremendous amount of power and functionality relies upon the Run command, something that Microsoft removed from its usual location in the Windows 10 Start Menu. Windows 10 hosts a large amount of variety tools that are difficult to remember the Windows 10 run commands. The Windows 10 includes “Run” which is a built-in app that can open any built-in app in windows and these commands are assisting the maximum to users without finding it on every edge of windows.
- Win 10 Run Commands
- Run Commands List
- Windows 10 Run Cmd On Startup
- Windows 10 Run Command History
- Windows 10 Run Cmd As Administrator By Default
All supported versions of Windows (server and client) have a set of Win32 console commands built in.
This set of documentation describes the Windows Commands you can use to automate tasks by using scripts or scripting tools.
To find information about a specific command, in the following A-Z menu, click the letter that the command starts with, and then click the command name.
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Prerequisites
The information that is contained in this topic applies to:
- Windows Server 2019
- Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel)
- Windows Server 2016
- Windows Server 2012 R2
- Windows Server 2012
- Windows Server 2008 R2
- Windows Server 2008
- Windows 10
- Windows 8.1
Command shell overview
The Command shell was the first shell built into Windows to automate routine tasks, like user account management or nightly backups, with batch (.bat) files. With Windows Script Host you could run more sophisticated scripts in the Command shell. For more information, see cscript or wscript. You can perform operations more efficiently by using scripts than you can by using the user interface. Scripts accept all Commands that are available at the command line.
Windows has two command shells: The Command shell and PowerShell. Each shell is a software program that provides direct communication between you and the operating system or application, providing an environment to automate IT operations.
PowerShell was designed to extend the capabilities of the Command shell to run PowerShell commands called cmdlets. Cmdlets are similar to Windows Commands but provide a more extensible scripting language. You can run Windows Commands and PowerShell cmdlets in Powershell, but the Command shell can only run Windows Commands and not PowerShell cmdlets.
For the most robust, up-to-date Windows automation, we recommend using PowerShell instead of Windows Commands or Windows Script Host for Windows automation.
Note
You can also download and install PowerShell Core, the open source version of PowerShell.
Playground peacemakers: Ask older students at your elementary school to casually patrol the playground while younger students are at recess. Free bullying programs for schools.
Caution
Incorrectly editing the registry may severely damage your system. Before making the following changes to the registry, you should back up any valued data on the computer.
Note
To enable or disable file and directory name completion in the Command shell on a computer or user logon session, run regedit.exe and set the following reg_DWOrd value:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftCommand ProcessorcompletionCharreg_DWOrd
To set the reg_DWOrd value, use the hexadecimal value of a control character for a particular function (for example, 0 9 is Tab and 0 08 is Backspace). User-specified settings take precedence over computer settings, and command-line options take precedence over registry settings.
Command-line reference A-Z
To find information about a specific Windows Command, in the following A-Z menu, click the letter that the Command starts with, and then click the Command name.
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z)
A
B
- bitsadmin
- bootcfg
C
- change
D
E
F
- fsutil
G
H
I
J
K
- ksetup
L
- logman
M
- manage-bde
N
Win 10 Run Commands
- nslookup
O
P
Q
R
- reg
S
- scwcmd
- secedit
T
U
V
- vssadmin-
W
- wbadmin
Run Commands List
X
Auto-complete is one feature that makes executing same or similar commands easy. Whether you are typing in the Command Prompt or on Run prompt if what you are typing matches with previously executed command, you save a lot of time. This small feature is so beautifully implemented that you can use the up, and down arrow keys to navigate through the set of commands in the run prompt or hit the down arrow button on the Run prompt to see all of them. During an active CMD session, you can also press F7 to see the history of the commands. If all of a sudden, you are not able to see the saved history, what do you do?
If your Run command is not saving History in Windows 10, then this post will show you how to enable it and make Windows save Run command History, by tweaking the Registry.
Run command not saving History
Windows 10 has implemented a ton of privacy features which turned of some of the features which were previously enabled by default. Issues around audio not working, microphone in webcams turned off are few popular ones.
The same has happened with the Run command history. Let’s figure out how to fix this:
- Click on the Start button, and on the left of it look for a cog icon. This will open Windows 10 Settings.
- Then click on Privacy > General
- Turn on the option which says ‘Let Windows Track app launches to improve Start and Search results.’
If this is greyed out for you, then you need to change one key in the Registry.
Type Regedit in Run prompt, and navigate to the following key-
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionExplorerAdvanced
Look for the Start_TrackProgs DWORD and then double-click to open and set the value to 1.
If the DWORD is not there, right click on empty area on the left pane, select New > DWORD. Enter the name as Start_TrackProgs and set value as 1.
Click OK, and reboot your computer.
Now type few commands in the Run prompt, and use the arrow keys to see if they are saved in the list. I am sure this is going to solve your problem.
Windows 10 Run Cmd On Startup
Whenever you update anything in Windows 10 Privacy settings, it has its effect at many places. So make sure you choose your options wisely as it may affect your day to day usage.
Windows 10 Run Command History
PS: If Start Menu is not showing Recent app history, you can enable it from the Show Apps settings
Windows 10 Run Cmd As Administrator By Default
Related Posts: